python数据拟合和分析
以下内容是我在进行webRTC拥塞控制部分进行训练集traces分析和生成的总结;举办方提供了一部分真实环境的数据,但我认为对于训练来说可能不够,因此需要自己生成一部分;
数据拟合
使用fitter库进行数据的拟合;大概的效果如下图所示:
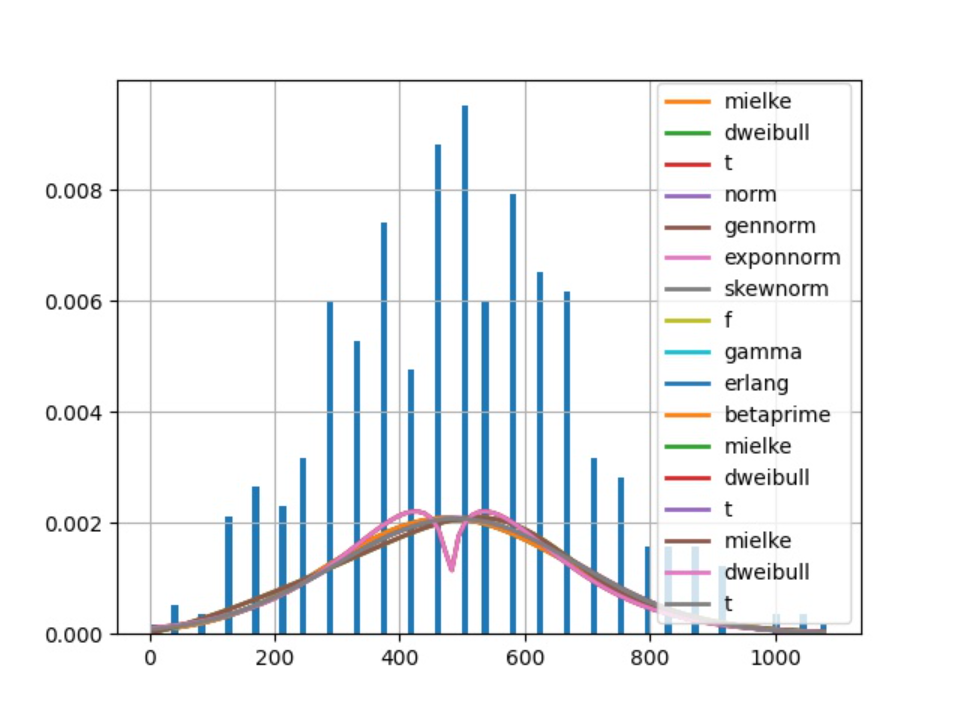
image-20210712190334719
fitter 库
fitter库的源码位置:https://github.com/cokelaer/fitter
安装fitter库: pip install fitter
fitter库的文档:https://fitter.readthedocs.io/en/latest/
fitter库使用案例
生成模拟数据:
1 | >>> # First, we create a data sample following a Gamma distribution |
使用 fitter库进行拟合:
1 | >>> # We then create the Fitter object |
它在使用fit函数的时候如果没有额外的参数会用scipy的80多个分布进行逐个拟合,默认的拟合时间是30秒;
fitter库参数
fitter
1
class fitter.fitter.Fitter(data, xmin=None, xmax=None, bins=100, distributions=None, timeout=30, density=True)
- data (list) –输入的样本数据;
- xmin (float) – 如果为None,则使用数据最小值,否则将忽略小于xmin的数据;
- xmax (float) – 如果为None,则使用数据最大值,否则将忽略大于xmin的数据;
- bins (int) – 累积直方图的组数,默认=100;
- distributions (list) – 给出要查看的分布列表。 如果没有,则尝试所有的scipy分布(80种),常用的分布distributions=[‘norm’,‘t’,‘laplace’,‘cauchy’, ‘chi2’,’ expon’, ‘exponpow’, ‘gamma’,’ lognorm’, ‘uniform’];
- verbose (bool) –
- timeout – 给定拟合分布的最长时间,(默认=10s) 如果达到超时,则跳过该分布。
1
2
3
4
5
6from fitter import Fitter
# may take some time since by default, all distributions are tried
# but you call manually provide a smaller set of distributions
f = Fitter(data, distributions=['gamma', 'rayleigh', 'uniform'])
f.fit()
f.summary()
进行fitter了之后可以调用一下函数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8f.fit() #fit(amp=1, progress=False, n_jobs=-1)
f.df_errors #返回这些分布的拟合质量(均方根误差的和)
f.fitted_param #返回拟合分布的参数
f.fitted_pdf #使用最适合数据分布的分布参数生成的概率密度
f.summary() #返回排序好的分布拟合质量(拟合效果从好到坏),并绘制数据分布和Nbest分布 summary(Nbest=5, lw=2, plot=True, method='sumsquare_error')
f.get_best(method='sumsquare_error') #返回最佳拟合分布及其参数
f.hist() #绘制组数=bins的标准化直方图
f.plot_pdf(names=None, Nbest=3, lw=2) #绘制分布的概率密度函数 plot_pdf(names=None, Nbest=5, lw=2, method='sumsquare_error')使用注意点
我在使用上述函数的时候f.hist()之后并没有出现图片,通过研究了它源码的issue发现比较保险的方法是import matplotlib,在 f.hist()之后加上plt.show()或者savefig()等操作,这样就能够显示图片了;
1
2
3
4
5import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
.....
f.hist()
plt.show()
plt.close()
实际使用的脚本
1 | # 批处理版 |
效果是批处理如下json格式的数据,会统计一个文件夹中的数据,给每一个数据绘图,并且把summary写道fit_result.txt中
1 | { |
数据折线图
1 | import matplotlib.pyplot as plt |
数据生成
经过查阅scipy的文档以及简单了看了fitter项目的源码,上面get_best()得到的形如:
1 | 'johnsonsu': (-0.43618926054816165, 1.8086581271068694, 26026.47774558232, 26854.12469365103) |
表示的参数为a, b, loc, scale;
具体含义见下图:

image-20210712190221706
通过上面fitter得到的参数,可以使用如下的代码进行数据的生成,生成的格式是narray:
1 | import scipy.stats as st |
数据筛选
1 | # 数据筛选 |
如果没有data1=data[:]的操作会出现无法删除的问题